Angel Danish on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
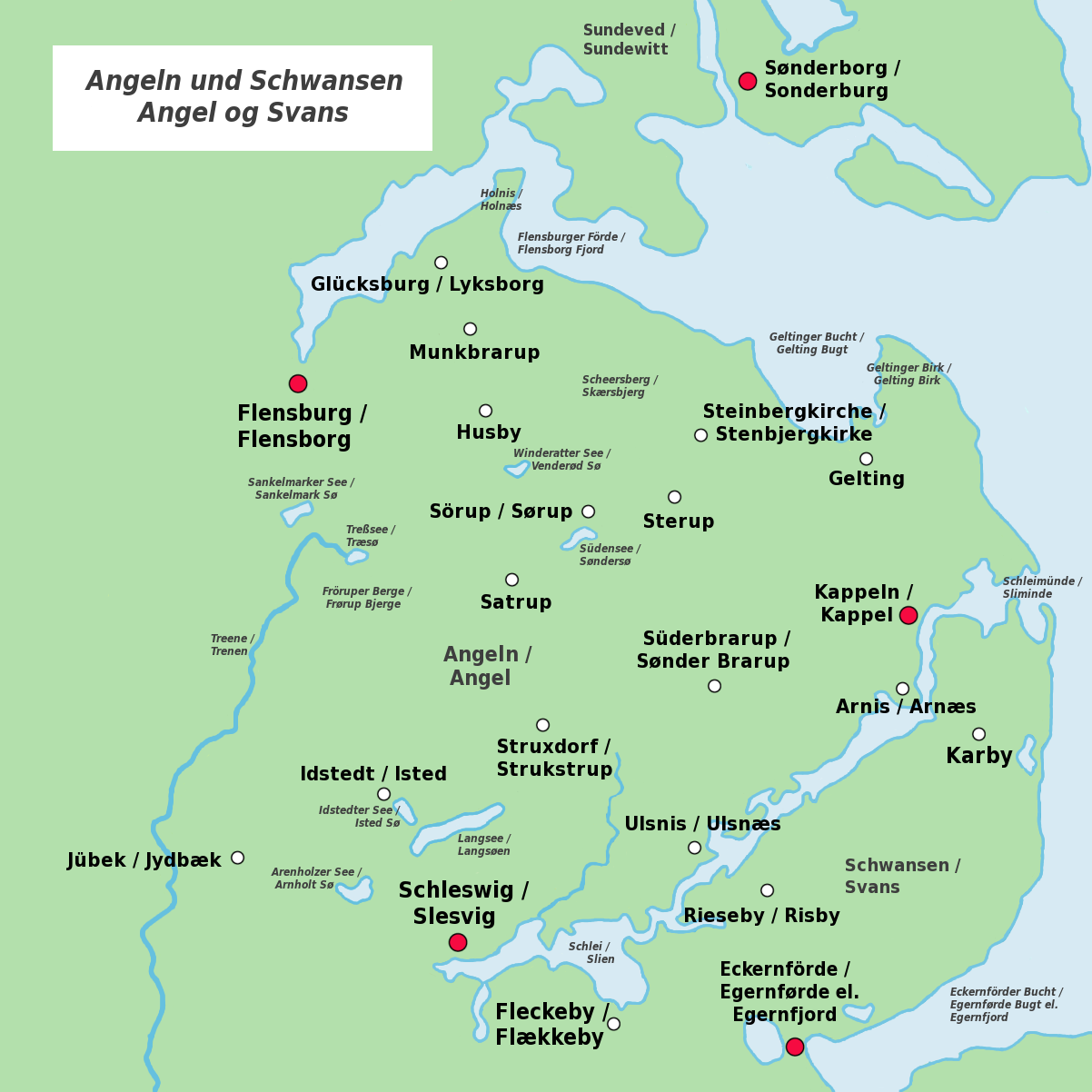 Angel Danish (German: ''Angeldänisch'', Danish: ''Angeldansk'' or ''Angelbomål'') was a variant of
Angel Danish (German: ''Angeldänisch'', Danish: ''Angeldansk'' or ''Angelbomål'') was a variant of
GB
GB
, 2. Bd. 1867
GB
) * Eiler Henning Hagerup: ''Om det danske Sprog i Angel'', Copenhagen/København 1854
GB
** ''Om det danske Sprog i Angel. Af E. Hagerup. Anden forgøgede Udgave, efter Forfatterens Død besörget af K. J. Lyngby. Ordbog. Sproglære. Sprogprøver'', Copenhagen/København 1867
GB
!-
GBGB
-->) Danish dialects {{Lang-stub
 Angel Danish (German: ''Angeldänisch'', Danish: ''Angeldansk'' or ''Angelbomål'') was a variant of
Angel Danish (German: ''Angeldänisch'', Danish: ''Angeldansk'' or ''Angelbomål'') was a variant of South Jutlandic
South Jutlandic or South Jutish (South Jutish: ; da, Sønderjysk; german: Südjütisch or Plattdänisch) is a dialect of the Danish language. South Jutlandic is spoken in Southern Jutland (''Sønderjylland''; also called Schleswig or Slesvig) o ...
spoken in the area of Angelia
In a poem by the Greek poet Pindar (5th-century BC), Angelia (Ancient Greek: Ἀγγελία ('Message') is mentioned as a daughter of the Greek messenger-god Hermes, where she is understood as "message" personified.A Greek–English Lexicons.v. ...
(German: ''Angeln;'', Danish: ''Angel'') and Swania (German: ''Schwansen'', Danish: ''Svansø'') in Southern Schleswig
Southern Schleswig (german: Südschleswig or ', da, Sydslesvig; frr, Söödslaswik) is the southern half of the former Duchy of Schleswig in Germany on the Jutland Peninsula. The geographical area today covers the large area between the Eider ...
partly until the 20th century. Both landscapes belonged to the Danish Duchy of Schleswig
The Duchy of Schleswig ( da, Hertugdømmet Slesvig; german: Herzogtum Schleswig; nds, Hartogdom Sleswig; frr, Härtochduum Slaswik) was a duchy in Southern Jutland () covering the area between about 60 km (35 miles) north and 70 km ( ...
until 1864, since then to Germany.
Characteristic of Angel Danish was among other the tonal pitch accent
A pitch-accent language, when spoken, has word accents in which one syllable in a word or morpheme is more prominent than the others, but the accentuated syllable is indicated by a contrasting pitch ( linguistic tone) rather than by loudness ( ...
(like in the Danish dialects
The Danish language has a number of regional and local dialect varieties. These can be divided into the traditional dialects, which differ from modern Standard Danish in both phonology and grammar, and the Danish accents, which are local varieties ...
of Als
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or Lou Gehrig's disease, is a neurodegenerative disease that results in the progressive loss of motor neurons that control voluntary muscles. ALS is the most com ...
and Langeland
Langeland (, ) is a Danish island located between the Great Belt and Bay of Kiel. The island measures 285 km2 (c. 110 square miles) and, as of 1 January 2018, has a population of 12,446.
as well as in Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
and Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
) and the fricative
A fricative is a consonant produced by forcing air through a narrow channel made by placing two articulators close together. These may be the lower lip against the upper teeth, in the case of ; the back of the tongue against the soft palate in t ...
for the hard ''G'' (like today in the Angel Low German
:
:
:
:
:
(70,000)
(30,000)
(8,000)
, familycolor = Indo-European
, fam2 = Germanic
, fam3 = West Germanic
, fam4 = North Sea Germanic
, ancestor = Old Saxon
, ancestor2 = Middle L ...
). There were also elevations from ''O'' to ''U'' (instead of Danish ''honning'' it was ''hunne'' in Angel Danish, cf. Icelandic ''hunang''). There were also older Nordic forms such as ''hvénner'' (German ''wenn'', Danish ''hvornår'', Old Norse ''hvenær''), ''mjølk'' (German ''Milch'', Danish ''mælk'', Old Norse ''mjólk'') or ''gut'' (German ''Junge'', Danish ''dreng'', Norwegian ''gutt''). However, there were also adoptions from German such as ''teller'' (Danish ''tallerken'') or ''hunger'' (Danish ''sult'')..
The dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of Linguistics, linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety (linguisti ...
has never been an official school or church language. In the 18th and 19th centuries, Angel Danish was increasingly replaced by Low and High German
The High German dialects (german: hochdeutsche Mundarten), or simply High German (); not to be confused with Standard High German which is commonly also called ''High German'', comprise the varieties of German spoken south of the Benrath and ...
. The last record of the dialect was made in northern Anglia in the 1930s. A travelogue from 1813 documents the language change from Angel Danish to German in Swania in the first half of the 19th century.„Die Landschaft auf der südlichen Seite der Schley heißt Schwansen ..Die Einwohner sind hier ebenfalls ächte Dänen, wenn auch ihre Mundart von einem Kopenhagener oder Norweger nicht leicht verstanden wird. ..Jetzt hört die Dänische Sprache auch beym Landvolke auf und die Plattdeutsche tritt ausschließlich an deren Stelle.“ From: Peter Treschow Hanson: ''Reise durch einen Theil von Sachsen und Dänemark in den letztverflossenen Jahren'', Altona 1813, p. 299, 300GB
References
Bibliography
* Harald Wolbersen: ''Der Sprachwechsel in Angeln im 19. Jahrhundert – Eine kulturhistorische Untersuchung zum Verlust der dänischen Varietät „Sønderjysk“ im Transformationsprozess zur Moderne'', Hamburg/Hamborg 2016, ISBN 978-3-8300-9212-4 * Harald Wolbersen: ''Die dänische Sprache in der Region Angeln'', in: Nordeuropa-Forum, Berlin 2015 * Georg Saß: ''Angeldänische Sprachdokumente'', in: Jahrbuch des Heimatvereins Angeln, Kappeln/Kappel 2005 * Bent Jul Nielsen und Magda Nyberg: ''Ordbog over den danske dialekt i Angel'', Copenhagen/København 1995 * Johannes Kok: ''Det Danske Folkesprog i Sønderjylland'', Copenhagen/København 1863–70 (1. Bd. 1863GB
, 2. Bd. 1867
GB
) * Eiler Henning Hagerup: ''Om det danske Sprog i Angel'', Copenhagen/København 1854
GB
** ''Om det danske Sprog i Angel. Af E. Hagerup. Anden forgøgede Udgave, efter Forfatterens Død besörget af K. J. Lyngby. Ordbog. Sproglære. Sprogprøver'', Copenhagen/København 1867
GB
!-
GB
-->) Danish dialects {{Lang-stub